| Section 2 » Family Blechnaceae |
Show/Hide Synonym
| taxonName | relationship | relatedTaxonName | relatedTaxonRefText | relComments |
|---|
|
|
|
| Anchistea virginica | = | Woodwardia virginica | | | | Anchistea virginica | = | Woodwardia virginica | Gleason and Cronquist (1991) | | | Anchistea virginica | = | Woodwardia virginica | Fernald (1950) | | | Anchistea virginica | = | Woodwardia virginica | Flora of North America (1993b, 1997, 2000, 2002a, 2002b, 2003a, 2004b, 2005, 2006a, 2006b, 2006c, 2007a, 2009, 2010) | | | Anchistea virginica | = | Woodwardia virginica | Gleason (1952) | | | Anchistea virginica | = | Woodwardia virginica | | | | Anchistea virginica | = | Woodwardia virginica | Kartesz (1999) | | | Anchistea virginica | = | Woodwardia virginica | | | | Anchistea virginica | = | Woodwardia virginica | Radford, Ahles, and Bell (1968) | | | Anchistea virginica | = | Woodwardia virginica | | | | Anchistea virginica | = | Woodwardia virginica | Flora of Virginia | | | Anchistea virginica | = | Woodwardia virginica | Wofford (1989) | | | Anchistea virginica | = | Woodwardia virginica | Wunderlin & Hansen Flora of Florida (3) | | | Source: Weakley's Flora |
|
| Author | (L.) C. Presl | |
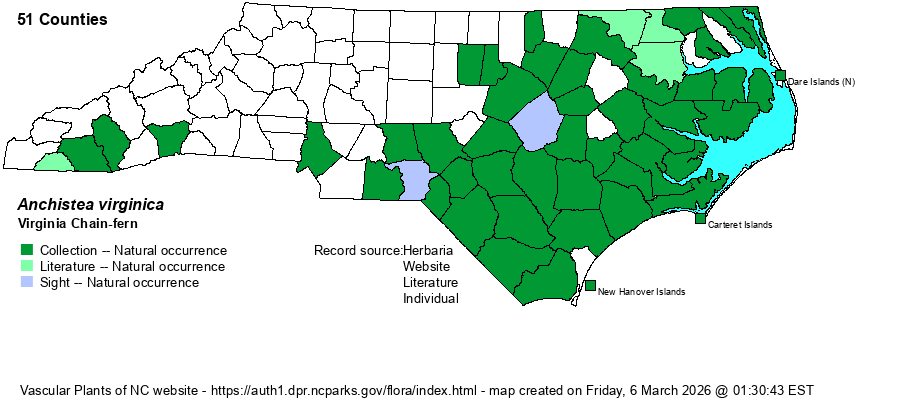
| Distribution | Throughout the Coastal Plain; ranges barely into the eastern and southern Piedmont, and disjunctly in the southern Mountains. Essentially absent in the northwestern half of the state.
This is an Eastern species with a somewhat bimodal range. It occurs in eastern Canada and the northeastern states, south to NY, OH, and northern IN. It then extends mainly in the Coastal Plain from southeastern MA south to southern FL and central TX, but is very rare from IL to WV and south to central GA and northern AR. | |
| Abundance | Common, to locally very common, in nearly all of the Coastal Plain, including the Sandhills; rare in the eastern and southern Piedmont, and very rare in the southern Mountains. | |
| Habitat | This is one of the more frequently seen ferns of strongly acidic wet soils in the Coastal Plain. It grows in peaty soils such as pocosins, blackwater bottomlands and swamps, blackwater streamheads, margins of Carolina bays, and other similar damp to wet sites in organic soils (mostly wooded and usually with sphagnum moss). | |
| Phenology | Fruits from June to September. | |
| Identification | This familiar Coastal Plain species has essentially just fertile fronds, each arisingly singly (not clumped), with a shiny purplish-brown stipe. The stipe is often 1 foot long, and the dark green and somewhat coriaceous (though not evergreen) blade is about 1-1.5 feet long and 6 inches wide. The blade is pinnate-pinnatifid, oblong to lanceolate in overall shape; there are 15-20 pairs of pinnae, somewhat opposite, each about 3 inches long. The sori are linear and are aligned along the midribs of the pinnules, and characteristically also along the rachis of the pinnae, on the undersides of the pinnae. If sori are not present, this species can be confused with some other ferns, especially Log Fern (Dryopteris celsa) and perhaps a few others. However, essentially all other similar species have the fronds growing in clumps, as opposed to arising singly from the ground. This is one of the first species to "green up" following a fire in pocosin habitats, easily spotted when most other vegetation is still blackened. | |
| Taxonomic Comments | The species was long known as Woodwardia virginica. The genus Woodwardia is now considered Eurasian, and certainly this species and the other "Woodwardia" in the East -- now Lorinseria areolata -- had very little in common.
| |
| Other Common Name(s) | None | |
| State Rank | S5 | |
| Global Rank | G5 | |
| State Status | | |
| US Status | | |
| USACE-agcp | | |
| USACE-emp | | |